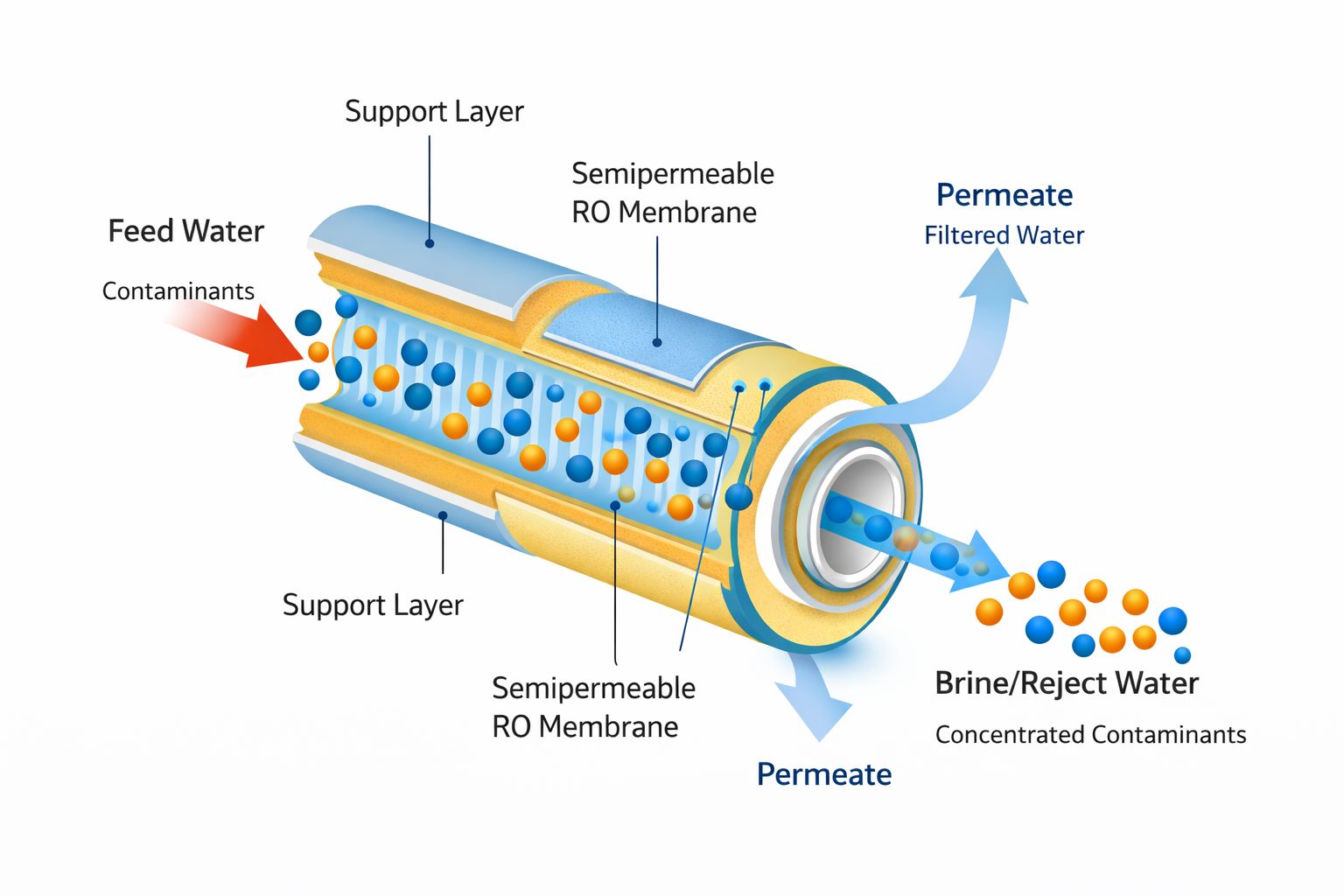
Reverse osmosis is one of the most effective water purification technologies used in residential homes today. Yet many homeowners still ask: how does a RO membrane work, and what makes it capable of filtering water down to 0.0001 microns?
If you’re considering a reverse osmosis water filter for your home, understanding how a RO membrane works reveals why this technology is trusted worldwide for producing clean, safe, and great-tasting drinking water.
What Is a Reverse Osmosis Membrane?
A reverse osmosis membrane is a semi-permeable barrier designed to remove extremely small contaminants from water. The membrane contains microscopic pores around 0.0001 microns in size, which allow water molecules to pass through while blocking dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria, and other impurities.
This level of filtration is far finer than standard water filter systems, making reverse osmosis particularly effective for drinking and cooking water. Understanding how a RO membrane works at this microscopic level helps explain why it’s the gold standard for home water purification.
How Does a RO Membrane Work?
To understand how a RO membrane works, it helps to break the process into stages.
Step 1: Pressure Is Applied
Incoming water is pushed against the RO membrane using household water pressure. This pressure forces water molecules toward the membrane surface.
Step 2: Selective Filtration
Only pure water molecules are small enough to pass through the membrane’s microscopic pores. Contaminants such as lead, arsenic, fluoride, salts, and dissolved minerals are too large and are rejected.
Step 3: Contaminants Are Flushed Away
The system carries rejected impurities away in a separate waste stream, preventing buildup on the membrane surface and maintaining filtration efficiency.
Step 4: Purified Water Is Stored
Filtered water is collected in a storage tank, ready for use at your dedicated drinking tap.
This process allows a reverse osmosis water filter to remove up to 99% of dissolved contaminants from drinking water.
Why 0.0001 Micron Filtration Matters
The 0.0001 micron pore size is what sets reverse osmosis apart from conventional filtration. This is the key to how a RO membrane works so effectively—at this level, the membrane can reduce:
- Heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic
- Fluoride and nitrates
- PFAS and chemical residues
- Dissolved salts and total dissolved solids (TDS)
- Bacteria and microorganisms
- Chlorine by-products affecting taste and odour
For Sydney homes concerned about water purity, this level of filtration offers exceptional protection at the point of use.
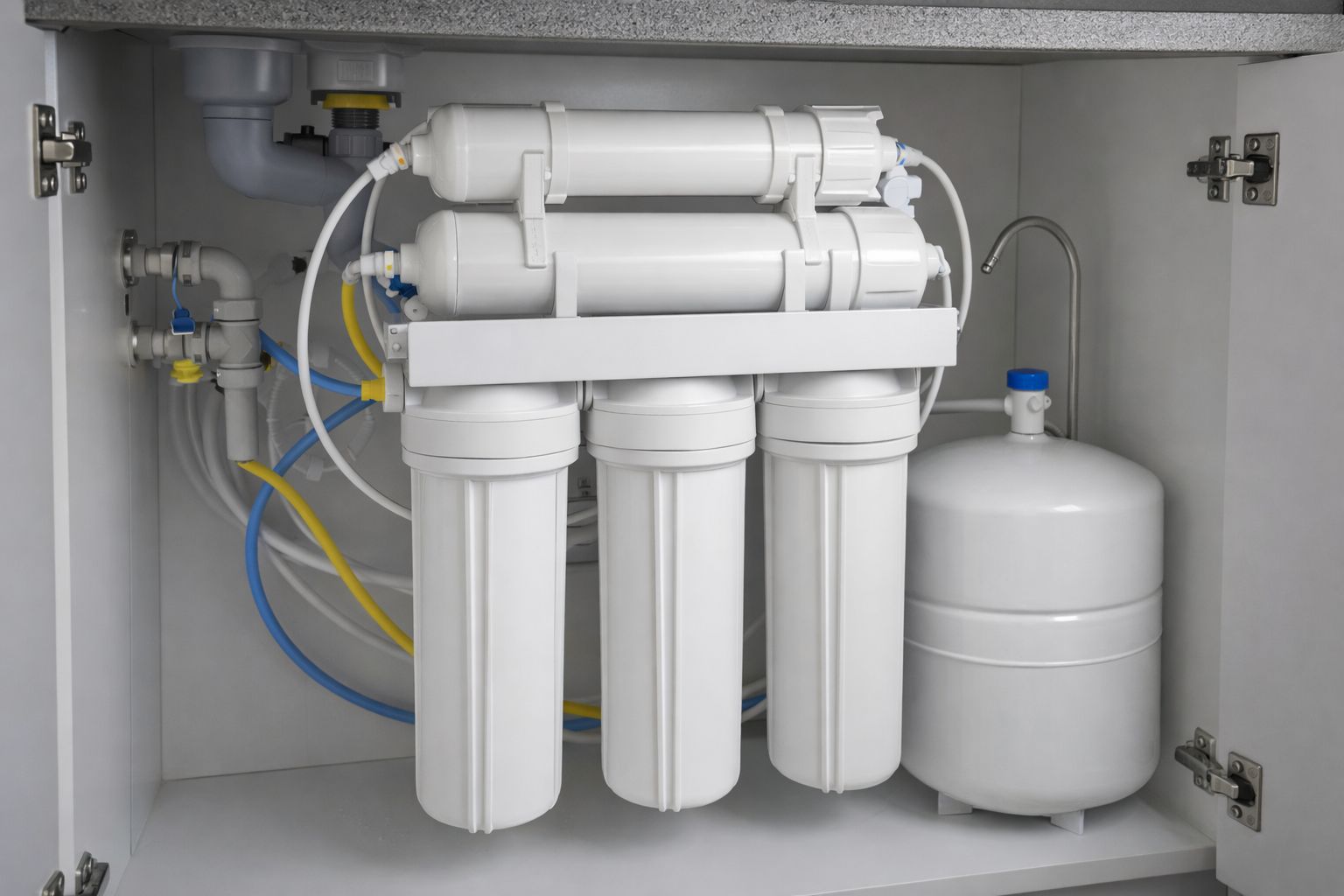
How RO Fits Into Residential Water Filter Systems
Once you understand how a RO membrane works at the molecular level, you’ll see why reverse osmosis systems are typically installed under the kitchen sink as part of a layered filtration approach. Many homeowners combine RO with other water filter systems, such as:
- Whole-house filtration for chlorine and sediment
- Carbon filtration for taste improvement
- UV treatment for bacterial protection
- RO membranes for ultra-fine purification
This combination ensures excellent water quality throughout the home, with maximum purity where it matters most, drinking and cooking.

What Makes RO Different From Standard Filters?
Standard carbon filters remove chlorine, odours, and some organic compounds, but they cannot filter dissolved solids at a molecular level. Reverse osmosis membranes use pressure-driven separation, allowing only water molecules to pass through.
This is why RO systems are often recommended when water testing identifies heavy metals, high TDS, or chemical contamination.
Is Reverse Osmosis Suitable for Sydney Homes?
While Sydney’s municipal water is treated to high standards, ageing infrastructure and regional variations can still affect water quality at the tap. A reverse osmosis system provides an extra layer of control, ensuring consistent water purity regardless of seasonal or supply changes.
For families, young children, or anyone sensitive to water taste or contaminants, RO filtration offers peace of mind and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a RO membrane work differently from carbon filters?
What contaminants can a reverse osmosis water filter remove?
Does reverse osmosis remove beneficial minerals?
How often should an RO membrane be replaced?
Does reverse osmosis affect water pressure?
Is RO filtration safe for children and families?
Can RO be combined with whole-house water filter systems?
Install a Reverse Osmosis System Today
Now that you understand how a RO membrane works to filter water down to 0.0001 microns, you can appreciate why a professionally installed reverse osmosis system is the ultimate solution for home water purity. Call Full House Water Filtration on 0404 613 998 to book a water assessment and find the right RO system for your Sydney home.